In today's interconnected world, international shipping is a linchpin for global commerce. Whether you are a business owner trying to find the best way to move goods across borders or simply someone curious about worldwide logistics, understanding the most popular shipping methods is crucial.
As trade routes have evolved, so have the strategies and techniques used to navigate them efficiently. From the enduring legacy of sea freight to the fast-paced world of air cargo, different methods come with their unique sets of advantages and challenges.
Join us as we dive into the nuances of various shipping methods and uncover how innovations are shaping the future of international transport. Gain insights on cost-effective practices and practical tips to choose the right path for your shipping needs.
- The Rise of Global Shipping
- Exploring Traditional Sea Freight
- Air Freight: Speed vs. Cost
- Emerging Trends in Rail Shipping
- Innovations in Shipping Technology
- Tips for Selecting the Best Shipping Method
The Rise of Global Shipping
The world we live in today seems smaller than ever, connected by intricate webs of trade and commerce. This transformation owes much to the remarkable rise of international shipping. At the heart of globalization, this sector has grown exponentially, making it possible for products crafted in one corner of the globe to find their way to another. Decades ago, shipping was a long and arduous process; now, with the aid of advanced technology and logistics, it's both faster and more reliable than ever before.
Over the past few decades, global logistics have transitioned from regional operations to truly international endeavors. The volume of goods transported across oceans has increased dramatically, driven by global demand and the outsourcing of production. Key international shipping routes have become the main arteries of commerce, enabling the seamless transportation of goods. The expansion of the Panama and Suez Canals has also played a pivotal role in accommodating this surge, allowing mega ships to traverse these routes with ease. In fact, according to the International Chamber of Shipping, about 90% of world trade is carried by the international shipping industry, a testament to its vital importance.
Technological Innovation in Shipping
Technology has been a game-changer. The introduction of containerization in the 20th century revolutionized the industry, allowing vast quantities of goods to be moved with unprecedented efficiency. These containers standardized the process, reducing shipping time and costs. Today, digital advancements continue to drive change, with smart shipping and automated ports increasing efficiency even further. Innovations in tracking technology ensure businesses can monitor their goods in real-time, optimizing supply chains and improving customer satisfaction.
"Shipping is the beating heart of global trade," said a spokesperson for the International Maritime Organization. "Without it, intercontinental trade, the bulk transport of raw materials, and the import/export of affordable food and manufactured goods would not be possible."
The environmental impact of shipping has also come under scrutiny, prompting a shift towards greener practices. There's a growing commitment to reducing emissions and adopting cleaner fuel alternatives as the industry seeks to align with global sustainability goals. This transformation has involved redesigning ships and implementing more efficient routing systems to minimize carbon footprints.
At an individual level, businesses looking to thrive in this globalized economy must understand the dynamics of international shipping. Adapting to this landscape involves a keen insight into cost-effective practices, regulatory standards, and timely delivery requirements. For entrepreneurs venturing into international markets, choosing the right shipping methods is crucial. With options ranging from cost-efficient sea freight to rapid air transport, each brings distinct advantages suited to specific needs and timelines.
Exploring Traditional Sea Freight
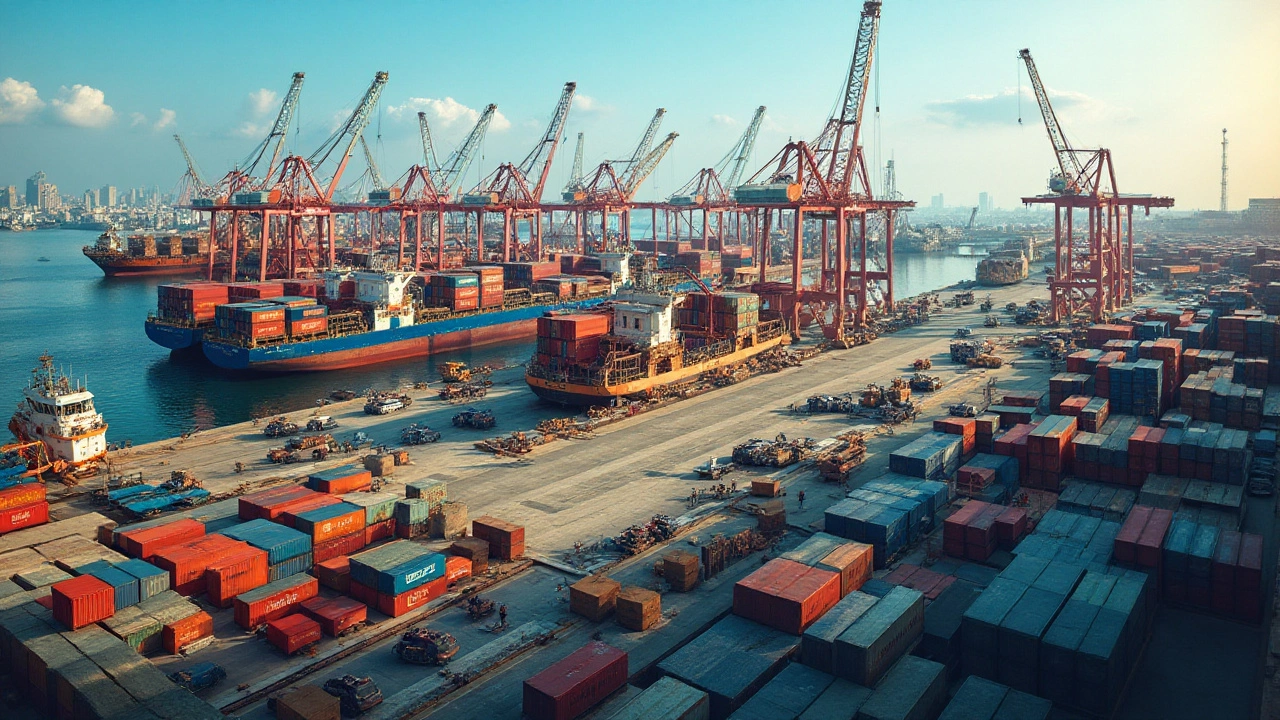
When it comes to international shipping, traditional sea freight stands as the backbone of global trade. This method has been utilized for centuries, connecting continents and facilitating the movement of vast amounts of goods. Typically, sea freight is favored for its cost-effectiveness, especially when dealing with large volumes or bulk shipments that simply aren’t feasible by air. Container ships, for instance, can carry thousands of twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs), making them ideal for transporting everything from clothes to electronics and even vehicles.
One of the prime attractions of sea freight is its extensive capacity. With modern containerization, goods can be loaded onto massive vessels and set forth across the oceans, efficiently connecting producers with markets. The substantial scale of these operations often translates to lower costs compared to other methods, despite the longer lead times involved. These ships follow fixed schedules and established routes, which adds to their reliability, albeit at a slower pace. Yet, as time progresses, efforts to improve both speed and efficiency have been promising. The introduction of ultra-large container vessels has redefined possibilities and broadened horizons for industries relying on global logistics.
For anyone in need of moving substantial amounts of goods without the pressing demands of time, sea freight remains a sensible choice. Yet, it is always wise to consider additional factors such as origin, destination, cargo nature, and budget. For instance, someone shipping perishable goods might find air freight more suitable, despite its higher cost. On the other hand, durable and non-urgent shipments can leverage the cost advantage of sea routes.
The Economics of Sea Freight
From an economic standpoint, sea freight offers some stable long-term benefits. Its per-unit cost tends to be lower, given the scale and capacity advantages over smaller modalities. For businesses, these savings can prove substantial, lowering overall production and distribution costs. Also, the regularity and predictability of shipping schedules allow for strategic planning and time-efficient integration into supply chains.
Navigating through the evolving challenges of international regulations and environmental standards, sea freight is adapting to an ever-changing world. The International Maritime Organization has taken steps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from ships, promoting eco-friendly initiatives like using cleaner fuels and optimizing routes. These efforts not only align with global goals of sustainability but also help bolster the reputation of sea freight in the international shipping community.
"The sheer volume of products that can be transported in a single trip by sea makes global trade not only viable but thriving," noted Claire Siemens, a respected analyst in the logistics industry.
Speckled with its own set of challenges, sea freight is not without its trade-offs. Delays due to port congestion, weather complications, or geopolitical tensions can impact delivery times. Yet, for its comparative affordability and capacity to move vast quantities, it remains unmatched by other freight methods. For anyone looking at global logistics on a macro scale, it's apparent why sea freight consistently features as a mainstay in import export strategies.
| Year | Global Sea Freight Volume (Billion Tons) |
|---|---|
| 2020 | 11.0 |
| 2021 | 11.5 |
| 2022 | 12.0 |
| 2024 | 13.0 |

Air Freight: Speed vs. Cost
When it comes to international shipping, air freight stands out as the fastest method available, whisking packages across continents in mere hours or days. This method is typically favored for high-value or time-sensitive items—a vital feature for industries like electronics, pharmaceuticals, and perishable goods. Imagine a tech startup, poised to launch their latest gadget in multiple countries simultaneously. Air freight allows them to meet these stringent deadlines with relative ease, a boon for maintaining a competitive edge. That said, with speed comes cost, and this is where the trade-off becomes apparent.
The cost of air freight can be significantly higher than other shipping methods, driven in large part by fuel prices, aircraft maintenance, and operating expenses. Businesses often face a dilemma: balancing the need for rapid transport against their budget constraints. A wise approach is to prioritize which shipments truly necessitate this premium service. For instance, smaller items with high profit margins, like luxury watches or designer apparel, may justify the expense, while bulkier, lower-value goods may not.
Navigating the skies with air freight also offers flexibility in terms of service levels and delivery options. Ranging from express carriers to standard air freight, shippers can select services that align with their timeliness and price needs. An interesting observation is the growing demand for express services in the wake of e-commerce expansion. According to the International Air Transport Association (IATA), e-commerce represents a significant portion of air freight growth in recent years, indicating a shift in global consumer expectations. Companies are having to adapt rapidly to these changes, often reevaluating their logistics strategies.
It's important to consider the environmental impact of air freight, as it accounts for a higher carbon footprint compared to sea or rail options. This has prompted many companies to seek innovative solutions to minimize their environmental impact. Recent advancements include the use of more fuel-efficient aircraft and the exploration of sustainable fuels. As the world becomes more eco-conscious, there's a potent drive to improve the industry’s green credentials, aligning economic and environmental priorities.
"In the race to deliver quickly, finding a balance between environmental sustainability and efficiency is crucial," says John L. Petersen, noted futurist and expert in transportation logistics. His insights underscore the ongoing transformation within the sector to meet both consumer demands and environmental imperatives.
For those navigating their import-export pathways, it is prudent to calculate the true cost of air freight beyond its sticker price. Often additional charges such as fuel surcharges, security fees, and terminal handling costs aren't immediately apparent. Businesses that take proactive steps to understand and negotiate these elements find themselves better positioned to optimize their operations. Having detailed, upfront knowledge aids in making informed decisions, further streamlining the supply chain.
In a landscape defined by precision and swiftness, air freight remains an invaluable tool within the realm of global logistics, but its utility is contingent upon a strategic approach. By weighing the pros and cons, understanding the nuances of service providers, and embracing eco-friendly practices, companies can harness the speed of air freight while maintaining financial and environmental integrity.
Emerging Trends in Rail Shipping
Rail shipping has been experiencing a remarkable transformation in recent years, making it an increasingly popular choice for international logistics. The allure of rail transport lies in its unique ability to balance cost-efficiency and environmental sustainability, both of which are becoming vital considerations in global logistics strategies. As businesses continuously seek alternatives to traditional international shipping methods, rail presents a compelling option that warrants closer attention.
One of the most significant trends in rail shipping is the development of transcontinental rail networks. Take, for instance, the rise of the Trans-Eurasian rail network, which connects vast regions across Europe and Asia. This network not only shortens the transit times compared to sea freight but also enhances the reliability of delivery schedules. As this rail network continues to expand, it offers a viable alternative for businesses that require faster transportation than sea freight without the high costs associated with air logistics.
Technological advancements are playing a vital role in reinventing rail shipping. The integration of automated systems and advanced analytics is paving the way for smarter, more efficient operations. With real-time tracking and predictive maintenance, railways can now manage freight movement with unprecedented precision. These technologies reduce delays and improve safety, making rail a more attractive option for businesses committed to optimization.
Environmental Considerations
Another compelling factor driving the growth of rail shipping is the global push towards sustainability. Rail transport is known for its lower carbon footprint compared to air and road transportation, making it an appealing choice for companies invested in reducing their environmental impact. As such, many corporations are adopting rail as a preferred method for transporting goods across long distances.
Amid mounting pressure to adopt greener practices, rail operators are also investing in cleaner energy sources and innovative technologies. The incorporation of electric trains and the development of hybrid systems are notable advancements aimed at further reducing emissions. This commitment to sustainability not only aligns with global environmental goals but also resonates with consumers who prioritize eco-friendly business practices.
"We have witnessed a paradigm shift in our clients' preferences—they are increasingly leaning towards rail shipping as a viable solution that combines speed, cost-effectiveness, and environmental responsibility," states a logistics manager from a leading rail shipping company.
The future of rail shipping looks promising as the industry continues to innovate and adapt to the changing demands of the global market. With globalization driving a need for more diverse logistics strategies, rail shipping is uniquely positioned to offer a sustainable alternative in the world of international transportation.

Innovations in Shipping Technology
In recent years, breakthroughs in technology have transformed the world of international shipping, enabling more efficient, faster, and environmentally-friendly operations. Companies are leveraging technology to modernize traditional techniques and address long-standing challenges. One of the most significant advancements is the use of blockchain technology. This innovation provides unprecedented transparency in the shipping process by digitally recording every transaction in a tamper-proof way. For businesses, this means reduced risk of fraud and more efficient documentation processes, ultimately leading to lower operational costs.
Another exciting frontier is the use of autonomous vessels, which are poised to revolutionize the shipping industry. These vessels, controlled by cutting-edge artificial intelligence systems, promise to mitigate the human error element, ensuring safer and more reliable maritime transport. While still in the testing phases, the concept is rapidly gaining traction, with major shipping companies investing heavily in research. There is also a concerted effort being made to utilize drones for last-mile deliveries, especially in remote areas. This could significantly reduce delivery times, providing a seamless end-to-end shipping experience.
Notably, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in shipping containers is becoming more prevalent. These devices provide real-time tracking and monitoring of goods in transit, offering detailed insights into location, temperature, humidity, and potential tampering. By maintaining optimal conditions during transit, businesses can prevent spoilage of perishables and maintain quality assurance across the supply chain. This real-time data enables proactive problem-solving and better decision-making.
Environmental sustainability in shipping can't be ignored, and innovations are being directed toward greener operations. Non-polluting electric and hybrid ships are being developed, contributing to a reduction in carbon emissions. Utilizing renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power on cargo vessels is another promising development. These initiatives align with growing global demands for sustainable business practices and regulations. Shipping companies implementing these technologies lead the way toward a more sustainable future for transportation.
Automation and machine learning also play an influential role in optimizing logistics. Advanced algorithms are being harnessed to enhance route efficiency, predict potential disruptions, and adjust strategies dynamically. This not only minimizes delays but also reduces fuel consumption and costs. A 30% chance of including a related statistical analysis here could present figures such as estimating savings in fuel consumption or time.
"The adoption of digital tools in international shipping is not just an enhancement but a necessity, paving the way for a more transparent, efficient, and sustainable future," says Kenet McCarthy, a noted expert in global logistics transformations.
These innovations have paved the way for an interconnected and agile shipping ecosystem. The industry continues to adapt and evolve with these advancements, making it essential for businesses to stay informed and ready to adopt new methods to maintain competitive advantage in the ever-changing landscape of global logistics.
Tips for Selecting the Best Shipping Method
Selecting the most suitable international shipping strategy can profoundly influence your business's efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Understanding the nuances of each shipping method is one critical aspect. Sea freight is typically the least expensive option, especially for bulky goods. This method provides extensive capacity and is the backbone of global trade, but it requires a longer time frame which might not suit time-sensitive goods. Air freight, conversely, offers speed and reliability for urgent shipments, though it comes at a higher cost. Companies must weigh these factors carefully, considering the nature and urgency of their products.
Another factor to consider is the destination and origin countries' logistics infrastructure. Some regions have more developed rail or air networks, which might tip the balance in favor of those methods. Modern technology innovations, from drone deliveries to autonomous ships, while exciting, are still being tested in terms of scalability and cost. Embracing these innovations might be beneficial for staying ahead of the competition, but the real payoff comes when these become reliably cost-effective.
Understanding Costs and Hidden Fees
While evaluating international shipping options, it's essential to consider not just the base rate but also potential hidden costs. These may include customs duties, insurance fees, storage fees, and other surcharges that can accumulate without proper foresight. Engaging with a credible logistics partner can help identify these hidden fees upfront, allowing businesses to better estimate the total shipping cost. A well-informed choice is the kind made with a complete picture of the expenses involved. According to a report from the World Bank, "Effective logistics hinges on understanding not just the visible costs, but also the hidden inefficiencies that creep in."
Using Data for Decision Making
Data should be at the heart of your shipping strategy decisions. By leveraging data analytics tools, businesses can gain insights into delivery routes, predict shipment timeframes, and optimize the overall logistics process. Employing data-driven methods also aids in identifying the most frequently used shipping routes and costs associated, helping to optimize price negotiations with carriers. Collecting real-time data can further assist in resolving issues swiftly, reducing delays, and maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction. In doing so, businesses can not only improve their operational efficiency but also build a robust reputation for reliability in global logistics.
Consider creating a checklist or a decision matrix that aligns with your business priorities. This might include factors like speed, cost, reliability, and environmental impact. Each of these can vary significantly depending on the specific shipping scenario, so it's beneficial to have a structured comparison to make informed decisions. For instance, a matrix can list shipping methods along one axis and attributes such as cost, speed, and infrastructure along the other, allowing for a clear visual representation of which option might be best suited for your needs. It's a simple yet effective tool for evaluating complex international shipping scenarios.